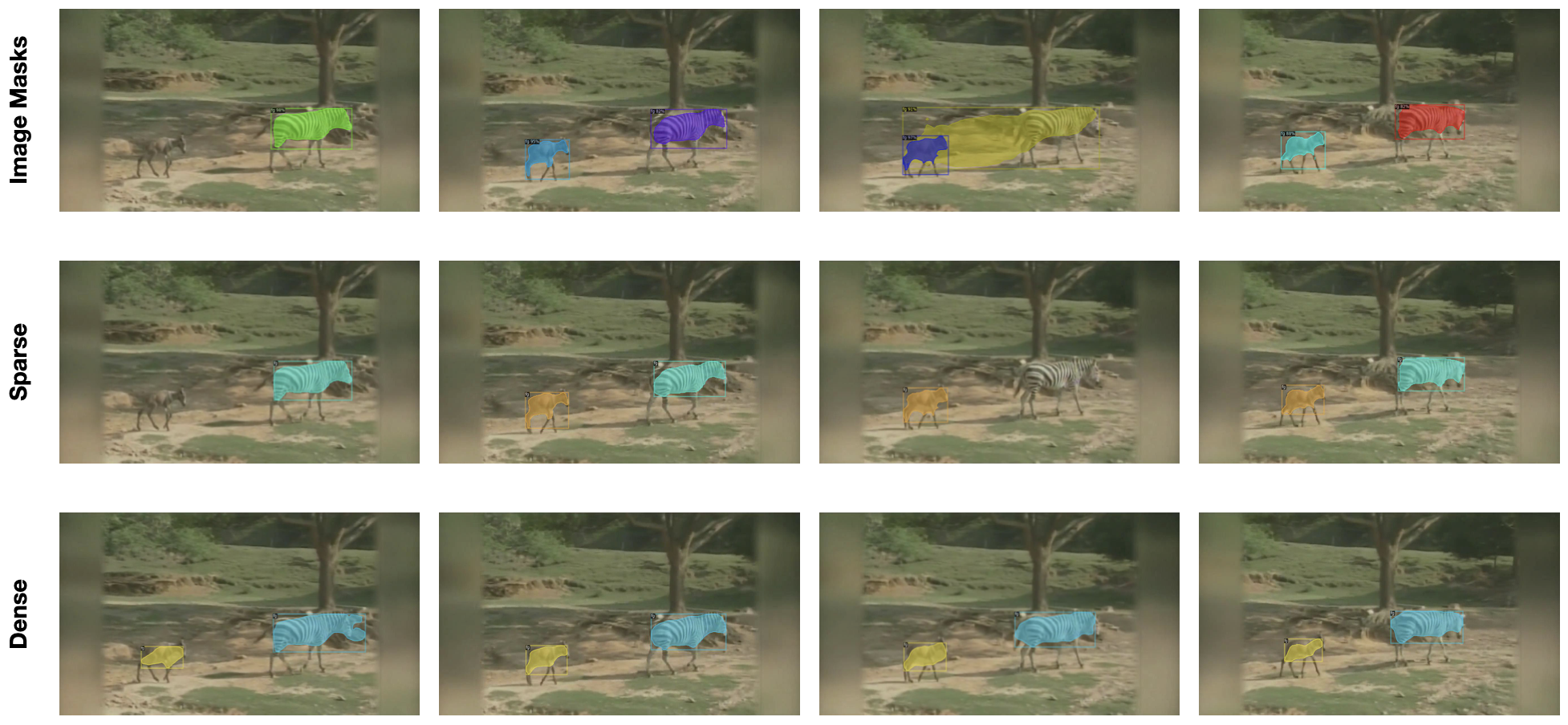
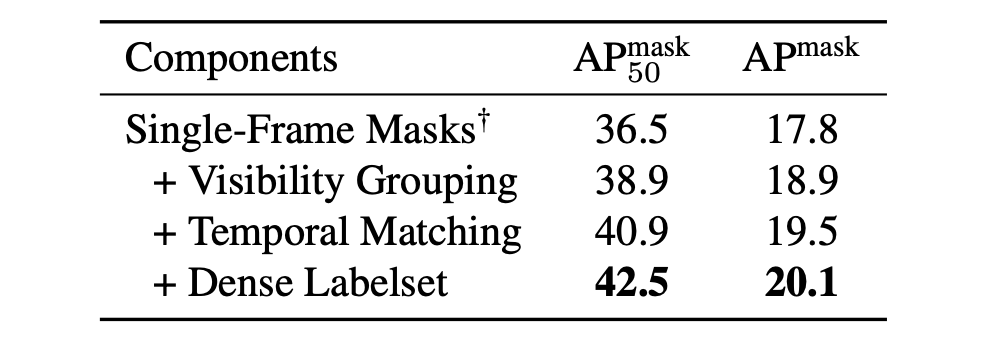
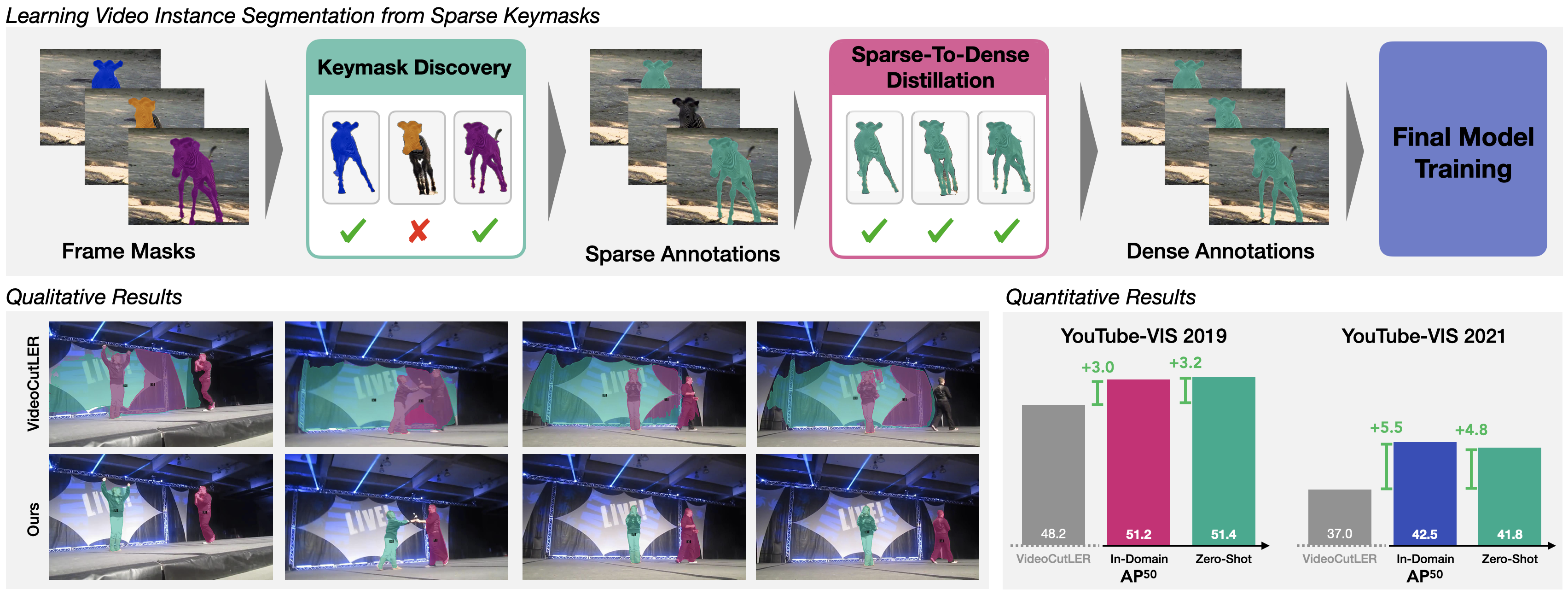
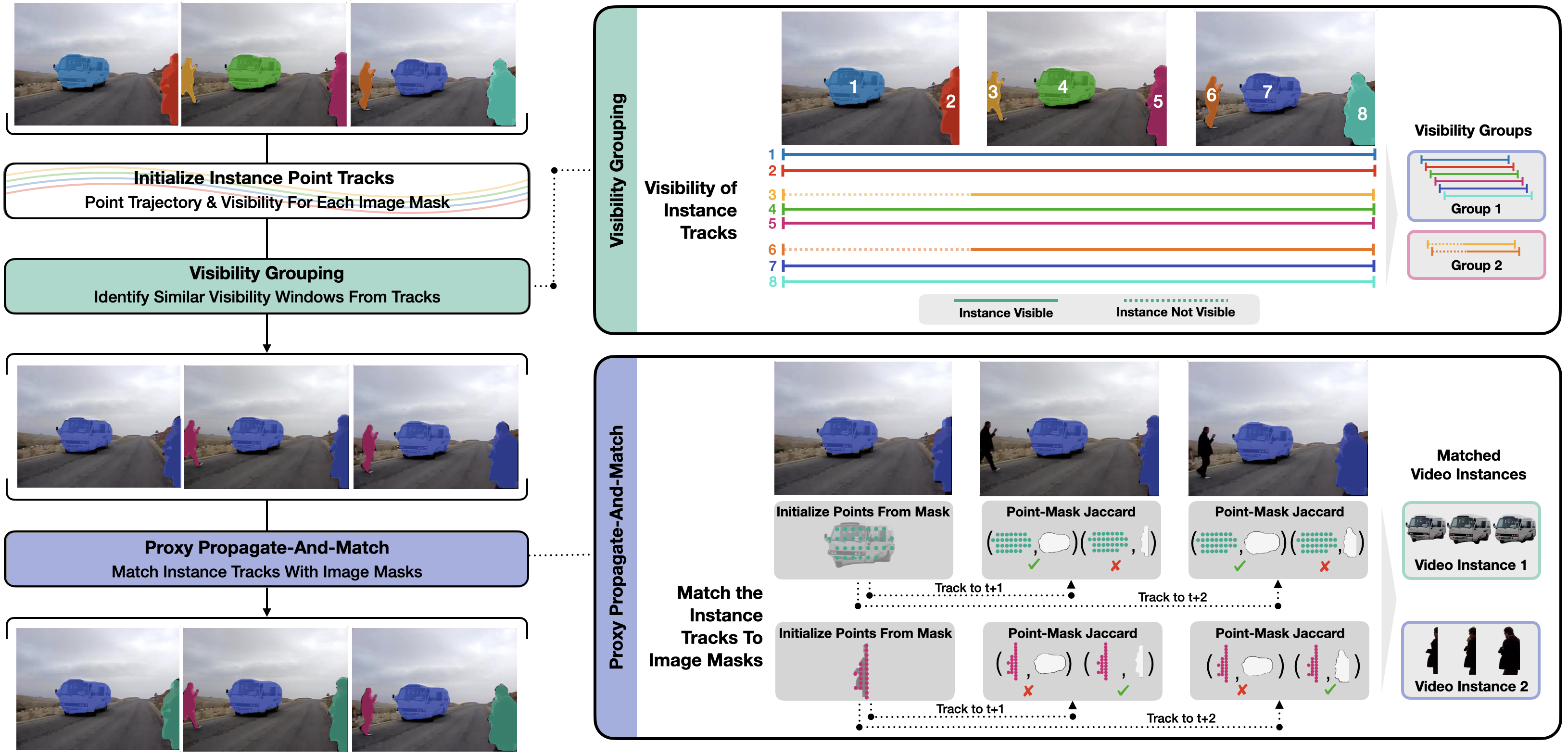
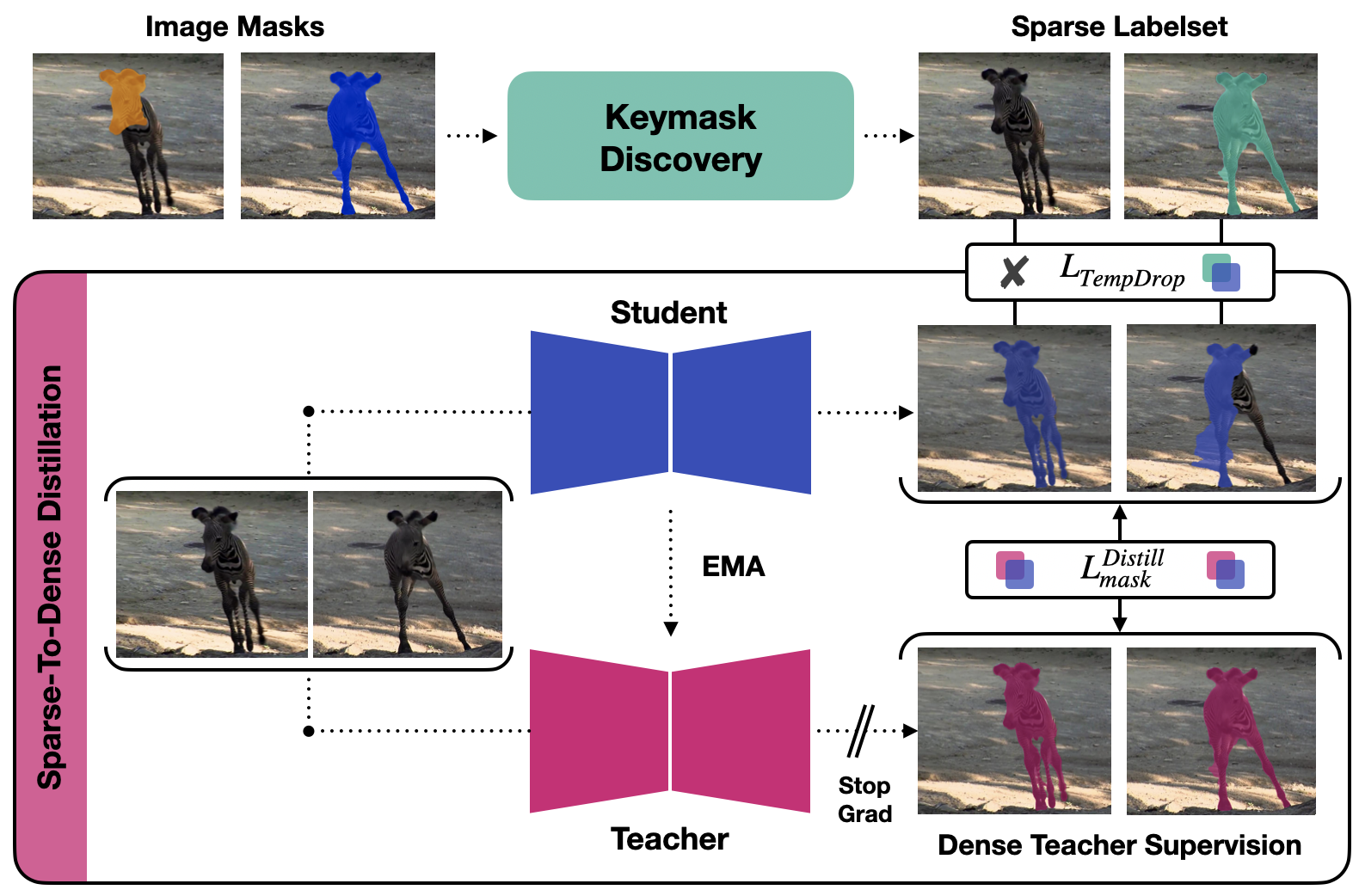
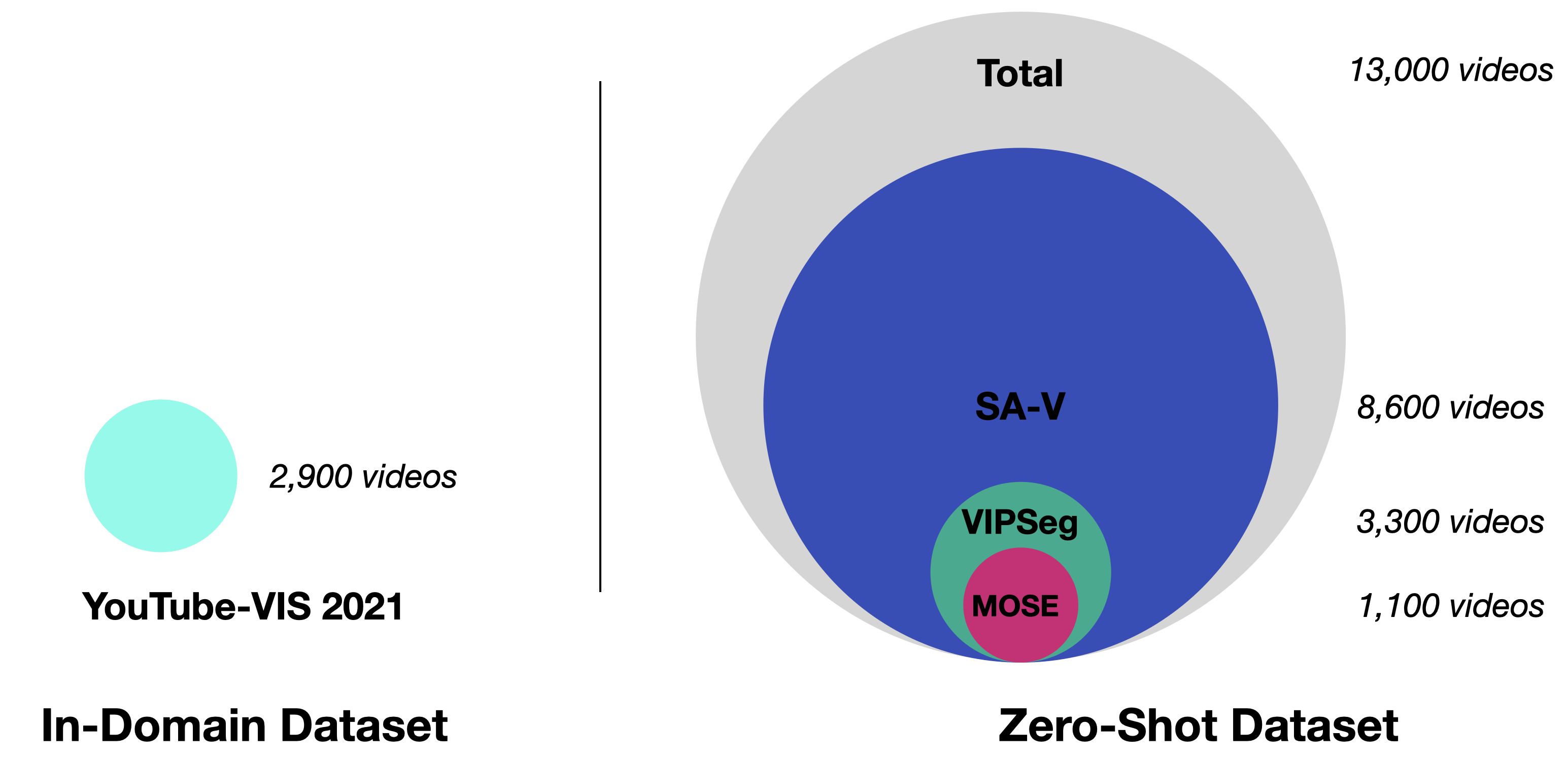
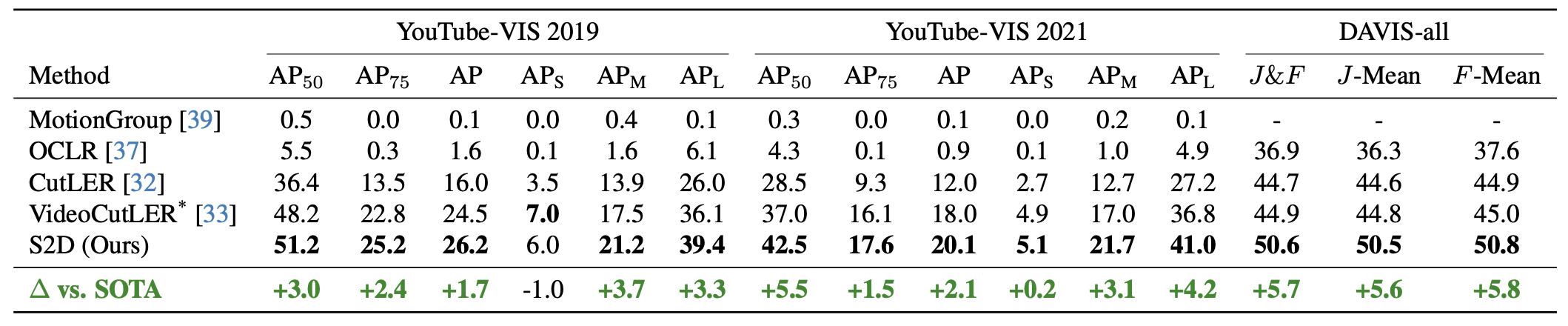
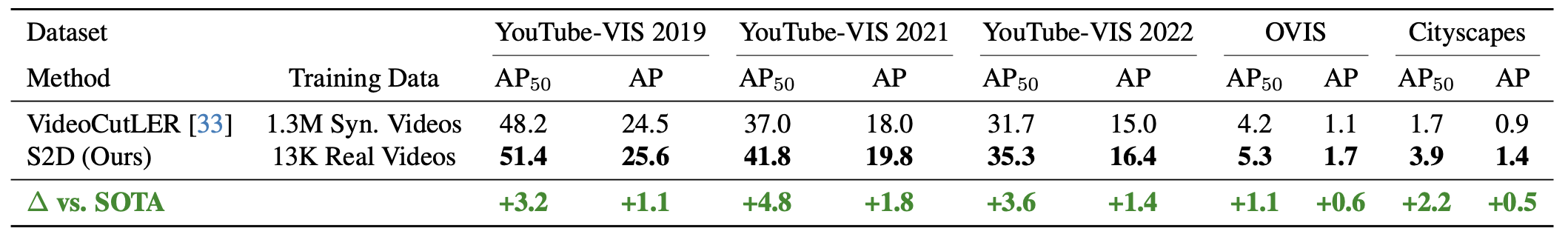
In recent years, the state-of-the-art in unsupervised video instance segmentation has heavily relied on synthetic video data, generated from object-centric image datasets such as ImageNet. However, video synthesis by artificially shifting and scaling image instance masks fails to accurately model realistic motion in videos, such as perspective changes, movement by parts of one or multiple instances, or camera motion. To tackle this issue, we propose an unsupervised video instance segmentation model trained exclusively on real video data. We start from unsupervised instance segmentation masks on individual video frames. However, these single-frame segmentations exhibit temporal noise and their quality varies through the video. Therefore, we establish temporal coherence by identifying high-quality keymasks in the video by leveraging deep motion priors. The sparse keymask pseudo-annotations are then used to train a segmentation model for implicit mask propagation, for which we propose a Sparse-To-Dense Distillation approach aided by a Temporal DropLoss. After training the final model on the resulting dense labelset, our approach outperforms the current state-of-the-art across various benchmarks.